
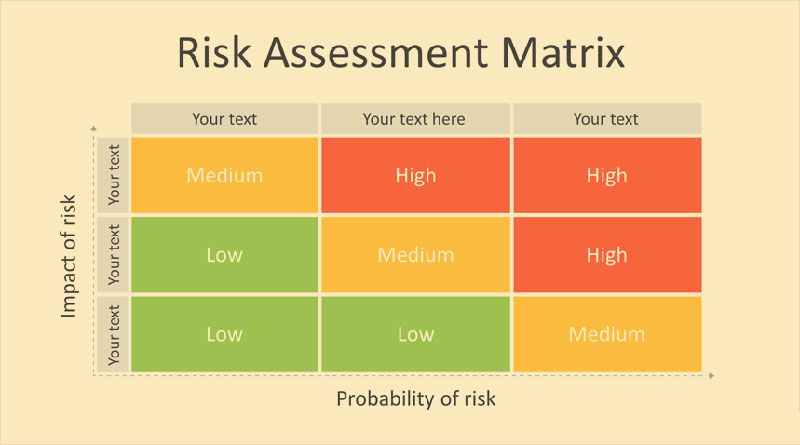
In addition, by using a scoring system of 1 – 5 or high, medium, low there is no valuable method to determine the risk’s cost of impact to your project. Qualitative risk assessment encourages scoring risks quickly with no concrete data for why an assessment was decided upon, just a subjective guess fitting into an ordinal scale (low, medium, high), or a cardinal scale (1 to 5). The use of likelihood is used solely and no quantitative assessment is completed. Risks are scored by an ordinal scoring process which excludes a quantitative risk analysis method altogether. An example is: there is a 70% chance of rain tomorrow.Ĭurrent bodies of knowledge tend to encourage qualitative scoring methods that offer little to no quantifiable information on project risks to be done first. Probability is a quantitative measurement of outcome.
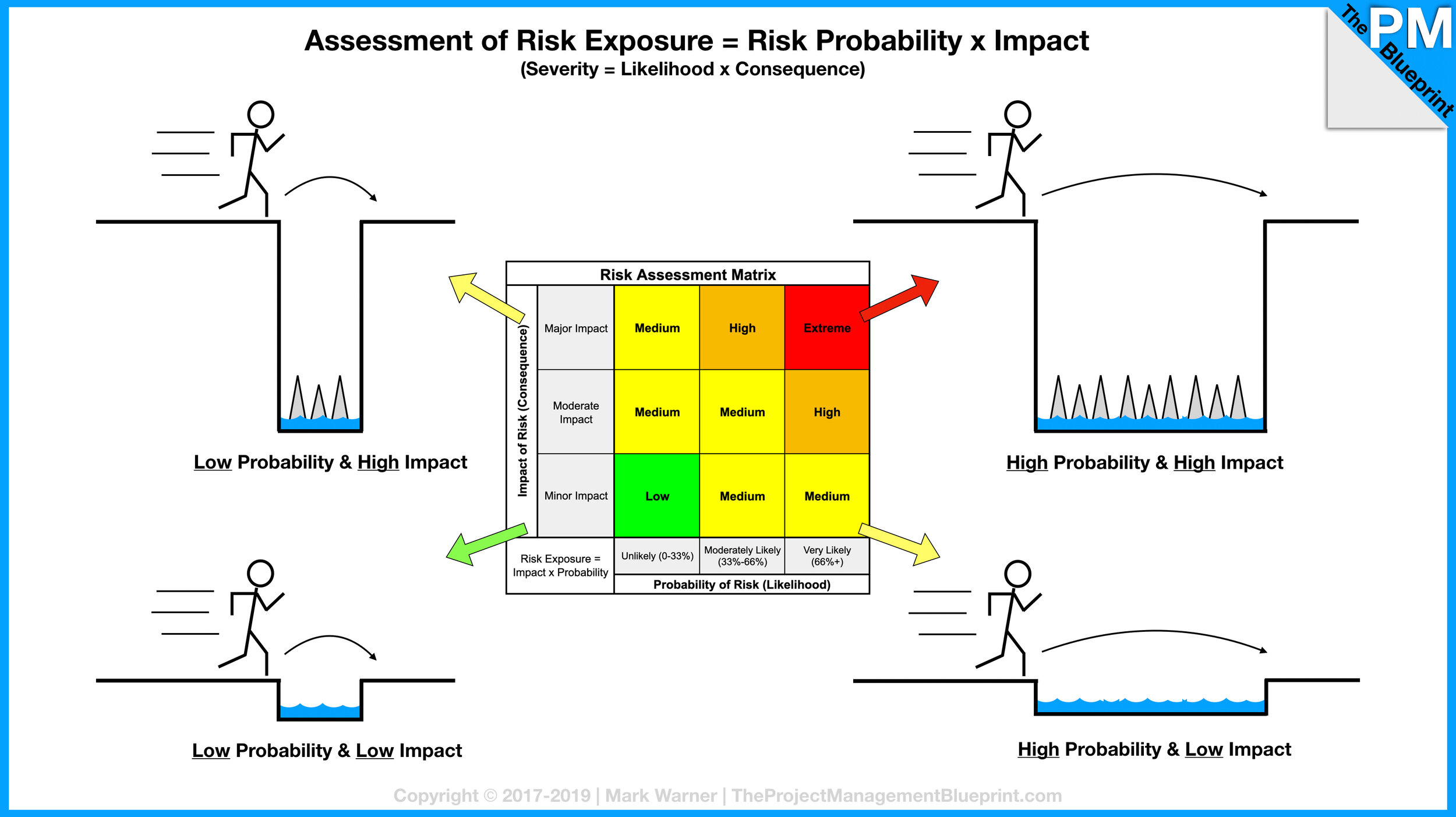
Probability refers to the percentage of possibilities that foreseen outcomes will occur based on parameters of values. An example is: there is a high likelihood of rain tomorrow. Likelihood is a qualitative assessment that is subjective with little objective measurement. By the way, these three assessment labels are also referred to as ordinal assessments since they only order the potential without providing any understanding of the difference between low, medium or high. Likelihood refers to the possibility of a risk potential occurring measured in qualitative values such as low, medium, or high. See our terms & privacy.įirst, let us discuss the meaning of the two terms and then discuss how they impact risk assessments. Risk analysis should be in some form of a quantitative predictive method which includes models that use historical information and expert knowledge. Let us start with the purpose of risk analysis which is to determine the risk probability of occurrence (RPO) and the risk cost of impact (RCI) which will determine the risk equivalent value (REV). But many PM still do not analyze risk in a quantifiable measure as they feel their risks are too complex or cannot be measured. Quantitative analysis, as opposed to qualitative analysis has a track record for improving decisions. However, a quantitative measurement is the only method that can result in a risk equivalent value (REV) to our projects. We have found that too many PM and project teams never measure risk quantitatively as they feel this method is too difficult to assess. The usage of likelihood as we will see from the definition below indicates risks are only managed by a qualitative measurement.
#Pmp risk probability and impact matrix series#
This article is a part of a series of articles under the Deliverable Centered Project Management series. But as PM and Risk Managers we need to be able to teach our teams good risk management processes and understanding this concept is critical. If you ask a mathematician to explain the difference between the two terms you might get a very long detailed answer that might confuse you even more. But are they? Both likelihood and probability expresses odds of occurrences but there is a clear difference in their meaning and use in the risk environment. What is the Difference Between Likelihood vs Probability in Risk Management? Many Project Managers (PM) and project teams confuse the terms of “likelihood” and “probability” and even consider them synonyms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
